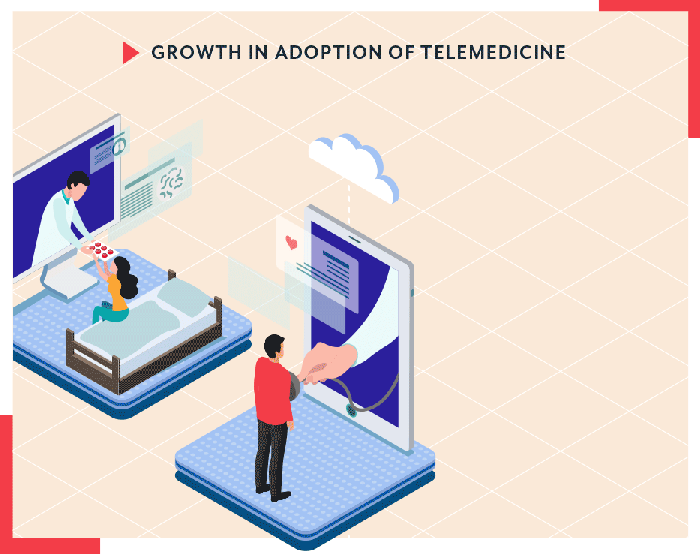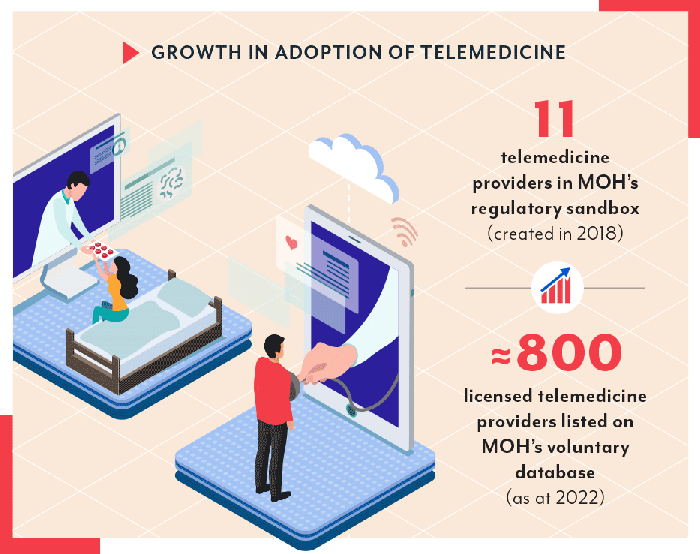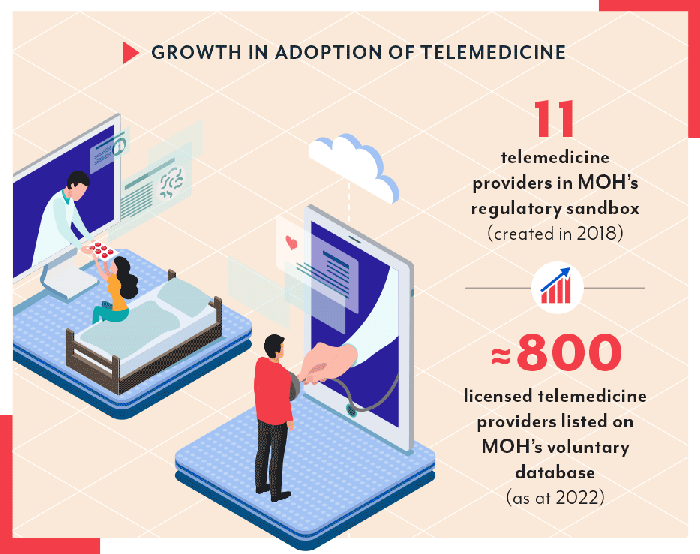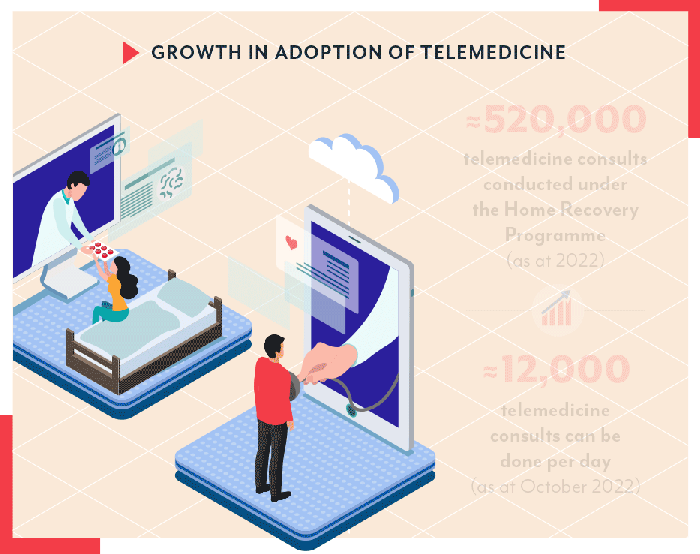
The healthcare landscape is rapidly evolving, with telemedicine playing an increasingly prominent role in delivering care. Healthcare alliances, strategic partnerships between healthcare organizations, are emerging as a key driver of telemedicine adoption and innovation. These alliances bring together diverse expertise, resources, and technology to address the challenges and opportunities presented by the convergence of telemedicine and traditional healthcare delivery.
This exploration delves into the various types of healthcare alliances, examining their specific goals and benefits in the context of telemedicine. We will explore how alliances can facilitate the development of new telemedicine models, enhance patient access to care, and improve overall healthcare outcomes. We will also address the challenges associated with data security, interoperability, and regulatory compliance in telemedicine alliances, highlighting the importance of robust frameworks and collaborative solutions.
The Convergence of Healthcare Alliances and Telemedicine
The healthcare industry is undergoing a period of rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving patient expectations, and the increasing focus on cost-effectiveness. Telemedicine, the delivery of healthcare services remotely using technology, has emerged as a significant force in this transformation, offering numerous benefits to both patients and providers. Healthcare alliances, formed by hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare organizations, play a critical role in leveraging the potential of telemedicine and navigating the challenges of this evolving landscape.
Benefits of Healthcare Alliances
Healthcare alliances offer several benefits, including:
- Enhanced Access to Care: By pooling resources and expertise, alliances can extend their reach to underserved communities and provide access to specialized care that might otherwise be unavailable. This is particularly relevant in rural areas or regions with limited healthcare infrastructure.
- Improved Efficiency and Cost Savings: Alliances can streamline operations, reduce administrative overhead, and leverage economies of scale to negotiate better prices for medical supplies and equipment. This can result in significant cost savings, which can be reinvested in improving patient care or expanding services.
- Increased Innovation and Collaboration: Alliances foster collaboration among healthcare providers, leading to the development of innovative solutions and the sharing of best practices. This can accelerate the adoption of new technologies, such as telemedicine, and improve the quality of care.
Types of Healthcare Alliances
Healthcare alliances are collaborative arrangements between two or more healthcare organizations, aiming to achieve shared goals and enhance patient care. These alliances can take various forms, each with distinct objectives and approaches.
Strategic Partnerships
Strategic partnerships are collaborative agreements between healthcare organizations to achieve mutual benefits. These alliances typically involve sharing resources, expertise, and technology to improve patient care, expand market reach, or gain competitive advantages.
- Shared Services: Organizations may collaborate to share services like billing, IT, or administrative functions, reducing operational costs and enhancing efficiency.
- Clinical Integration: Partnering to develop integrated care models, such as accountable care organizations (ACOs), to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs.
- Research and Development: Collaborating on research projects, clinical trials, or technology development to advance medical knowledge and innovation.
Joint Ventures
Joint ventures involve the creation of a new entity by two or more healthcare organizations, combining their resources and expertise to pursue a specific goal. Joint ventures are often used to expand into new markets, develop new products or services, or enter into new areas of healthcare delivery.
- Jointly Owned Facilities: Partnering to build or operate new hospitals, clinics, or other healthcare facilities to expand access to care.
- Developing New Products or Services: Collaborating to create new technologies, pharmaceuticals, or healthcare services that address unmet patient needs.
- Market Expansion: Partnering to enter new geographic markets or patient populations to increase market share.
Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions involve the combination of two or more healthcare organizations into a single entity. This can be achieved through mergers, where organizations combine on an equal footing, or acquisitions, where one organization takes over another.
- Consolidation: Combining operations to achieve economies of scale, reduce administrative costs, and gain market dominance.
- Expansion: Acquiring other organizations to expand geographic reach, gain access to new technologies, or diversify services.
- Market Leadership: Achieving a dominant position in a particular market segment to gain pricing power and influence.
Examples of Successful Healthcare Alliances in Telemedicine
Several healthcare alliances have successfully implemented telemedicine solutions to enhance patient care and access.
- Mayo Clinic and Teladoc: This strategic partnership provides virtual care services to Mayo Clinic patients through Teladoc’s telehealth platform, offering 24/7 access to medical professionals.
- Cleveland Clinic and IBM Watson Health: This alliance leverages IBM’s Watson Health technology to analyze patient data and provide personalized insights to improve diagnosis and treatment plans.
- MercyOne and Medtronic: This joint venture developed a remote patient monitoring program using Medtronic’s technology to track patients with chronic conditions, enabling early intervention and improved outcomes.
Challenges and Opportunities

The convergence of healthcare alliances and telemedicine presents a plethora of opportunities for innovation and improved patient care. However, there are significant challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the successful integration of telemedicine within these alliances.
Challenges in Integrating Telemedicine
Navigating the integration of telemedicine into healthcare alliances presents a unique set of challenges. These challenges stem from a complex interplay of technological, regulatory, and logistical factors.
- Interoperability and Data Security: One of the most significant hurdles is ensuring seamless data exchange between different healthcare systems. Different electronic health record (EHR) systems often use incompatible formats, making it difficult to share patient information across various providers. This lack of interoperability can hinder the flow of critical medical data, impacting patient care and potentially compromising data security.
- Regulatory Compliance: Telemedicine operates within a complex regulatory landscape, with varying laws and regulations across different jurisdictions. Healthcare alliances must navigate these regulations to ensure compliance and avoid legal issues. This includes obtaining necessary licenses, adhering to privacy laws like HIPAA, and understanding the specific requirements for telemedicine services in each region.
- Cost and Infrastructure: Implementing telemedicine requires significant investments in technology, infrastructure, and training. The cost of acquiring and maintaining telemedicine equipment, developing secure communication channels, and training staff can be a barrier for some healthcare alliances.
- Patient Acceptance and Accessibility: While telemedicine offers convenience, some patients may have reservations about receiving care remotely. Ensuring patient acceptance requires addressing concerns about privacy, data security, and the quality of care delivered through virtual means. Additionally, access to reliable internet and technology can be a challenge for some patients, particularly in underserved communities.
- Reimbursement Models: Reimbursement for telemedicine services can be complex and inconsistent. Healthcare alliances need to navigate the evolving landscape of reimbursement policies to ensure financial sustainability.
Data Security and Interoperability Risks
The convergence of telemedicine and healthcare alliances raises significant concerns about data security and interoperability.
- Data Breaches: The interconnected nature of telemedicine systems increases the risk of data breaches. Unauthorized access to sensitive patient information could have devastating consequences, impacting patient privacy and trust in the healthcare system.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring the integrity of medical data is crucial for accurate diagnoses and treatment plans. Telemedicine systems must be robust enough to prevent data manipulation or corruption, ensuring the reliability of information shared between providers.
- Data Sharing and Privacy: Healthcare alliances must establish clear protocols for data sharing between participating providers. Balancing the need for information exchange with patient privacy is a critical challenge, requiring strict adherence to regulations like HIPAA.
Opportunities for Innovation and Growth
Despite the challenges, telemedicine offers exciting opportunities for innovation and growth within healthcare alliances.
- Enhanced Patient Care: Telemedicine can provide patients with greater access to specialized care, particularly in rural or underserved areas. It can also facilitate remote monitoring, allowing for early detection of health issues and proactive management of chronic conditions.
- Improved Efficiency and Cost Savings: Telemedicine can streamline care delivery processes, reducing travel time for patients and freeing up resources for healthcare providers. By minimizing unnecessary visits, telemedicine can potentially lead to cost savings in the healthcare system.
- New Service Offerings: Healthcare alliances can leverage telemedicine to develop new service offerings, such as virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and telehealth-based mental health services. This expansion of services can attract new patients and create new revenue streams.
- Data-Driven Insights: Telemedicine generates a wealth of data that can be used to analyze patient outcomes, identify trends, and improve healthcare delivery. By leveraging data analytics, healthcare alliances can gain valuable insights into patient needs and develop more personalized care plans.
Case Studies
The convergence of healthcare alliances and telemedicine has led to numerous successful collaborations that have demonstrably improved patient care and outcomes. These case studies highlight the strategies, challenges, and lessons learned from these partnerships, showcasing the transformative impact of telemedicine on patient satisfaction, cost reduction, and healthcare access.
Case Study 1: Mayo Clinic and Teladoc
This alliance between the Mayo Clinic, a renowned healthcare provider, and Teladoc, a leading telemedicine platform, exemplifies the successful integration of telemedicine into a comprehensive healthcare system. The partnership has focused on expanding access to specialized care, particularly for patients in rural areas, through virtual consultations and remote monitoring.
Strategies
- The Mayo Clinic leveraged Teladoc’s established telemedicine infrastructure to provide virtual consultations with Mayo Clinic specialists.
- The partnership focused on integrating telemedicine into existing workflows, ensuring seamless transitions between in-person and virtual care.
- Both organizations collaborated on developing protocols and training materials for clinicians and patients to ensure effective utilization of telemedicine services.
Challenges
- The initial challenge was to ensure the security and privacy of patient data shared through the telemedicine platform.
- Integrating telemedicine services into existing workflows and patient records required careful coordination and communication between the two organizations.
- The alliance had to address concerns about the potential for increased healthcare costs associated with telemedicine.
Lessons Learned
- The importance of robust security and privacy measures for patient data was paramount.
- Integrating telemedicine into existing workflows and patient records was crucial for successful adoption.
- The alliance demonstrated that telemedicine can be cost-effective, particularly for specialized care and remote patient monitoring.
Impact
- The alliance expanded access to Mayo Clinic specialists for patients in rural areas, reducing travel time and costs.
- Telemedicine services contributed to improved patient satisfaction by offering convenient and accessible care options.
- The partnership helped to reduce healthcare costs by minimizing the need for expensive in-person visits for certain consultations and follow-ups.
Case Study 2: Cleveland Clinic and Anthem
The Cleveland Clinic, a leading academic medical center, partnered with Anthem, a major health insurer, to leverage telemedicine for chronic disease management and preventative care. This alliance aimed to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs by providing virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and educational resources for patients with chronic conditions.
Strategies
- The partnership focused on developing a comprehensive telemedicine program for chronic disease management, including diabetes, heart failure, and hypertension.
- The alliance utilized telehealth technologies for remote patient monitoring, enabling clinicians to track patient progress and intervene early if needed.
- They created educational resources and support groups for patients, empowering them to manage their conditions effectively.
Challenges
- The alliance faced challenges in ensuring patient engagement and adherence to telemedicine services.
- Integrating telemedicine services into existing workflows and patient records required careful planning and coordination.
- The partnership had to address concerns about the potential for increased healthcare costs associated with telemedicine.
Lessons Learned
- Patient engagement and adherence to telemedicine services were crucial for success.
- Integrating telemedicine into existing workflows and patient records was essential for seamless adoption.
- The alliance demonstrated that telemedicine can be cost-effective for managing chronic conditions and reducing hospital readmissions.
Impact
- The partnership improved patient outcomes by providing timely and personalized care for chronic conditions.
- Telemedicine services enhanced patient satisfaction by offering convenient and accessible care options.
- The alliance contributed to cost reduction by reducing hospital readmissions and improving disease management.
Future Trends
The convergence of healthcare alliances and telemedicine is poised to reshape the landscape of healthcare delivery, driven by technological advancements and evolving patient expectations. This section explores the future direction of these alliances and the impact of emerging technologies on their role in telemedicine.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The rapid evolution of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain is set to significantly influence the future of telemedicine alliances.
- AI-powered diagnostics and treatment recommendations: AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets of patient information, medical literature, and clinical trial data to provide accurate and personalized diagnoses and treatment plans. This can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of telemedicine consultations, enabling healthcare providers to deliver more informed care remotely. For instance, AI-powered chatbots can assist patients with initial symptom assessment, scheduling appointments, and providing basic health information, freeing up healthcare professionals for more complex cases.
- Blockchain for secure data management and interoperability: Blockchain technology can facilitate secure and transparent data sharing between healthcare providers, patients, and insurance companies within telemedicine alliances. This can improve patient privacy, streamline administrative processes, and enable seamless data exchange for improved patient care. For example, blockchain can be used to create a secure and tamper-proof record of patient medical history, ensuring data integrity and reducing the risk of fraud.
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) for immersive patient experiences: VR and AR technologies can enhance patient engagement and provide more interactive and personalized telemedicine experiences. VR simulations can be used for training healthcare professionals, while AR applications can overlay real-time information on patient data, enabling remote guidance during procedures.
Product Creation
Healthcare alliances are increasingly turning to product creation as a way to leverage their combined expertise and resources to develop innovative solutions that address unmet needs in the healthcare industry. This collaborative approach allows partners to pool their knowledge, technology, and market reach to create products that are more effective, efficient, and accessible.The process of product creation within alliances is characterized by a high degree of collaboration and shared expertise.
Partners work together to define product requirements, develop prototypes, conduct testing, and bring products to market. This collaborative approach fosters innovation by allowing different perspectives and expertise to be brought to bear on the product development process.
The Role of Technology and Data Analytics
Technology and data analytics play a crucial role in the product development process within healthcare alliances. These tools enable partners to gather insights from patient data, identify trends, and develop personalized solutions. For example, alliances may use data analytics to identify patients at risk for certain diseases or to develop predictive models that can help healthcare providers optimize patient care.
Examples of Successful Product Creation
Several healthcare alliances have successfully created innovative products in various industries.
- The Mayo Clinic and IBM Watson Health partnered to develop a cognitive computing platform that helps healthcare providers diagnose and treat patients more effectively. The platform leverages IBM Watson’s artificial intelligence capabilities to analyze vast amounts of medical data and provide insights to clinicians.
- The American Medical Association (AMA) and the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) collaborated to develop a set of quality measures for telehealth services. These measures provide a framework for assessing the quality of telehealth services and ensuring that patients receive high-quality care.
Bed and Breakfast Inns

Bed and breakfast inns, often charming and steeped in local history, offer a unique experience for travelers seeking an intimate and authentic stay. However, their success hinges on creating a memorable and enriching guest experience. Strategic alliances with local businesses can play a crucial role in enhancing this experience, driving tourism, and generating revenue for both parties.
Partnerships for Enhanced Guest Experience
Strategic alliances between bed and breakfast inns and local businesses can significantly enhance the guest experience. By collaborating, these businesses can offer a more comprehensive and engaging stay for travelers.
- Exclusive Packages: Bed and breakfast inns can partner with local attractions, restaurants, and shops to create exclusive packages that offer discounts or complimentary services. These packages provide guests with a curated experience, making their stay more enjoyable and value-driven.
- Local Expertise: Inns can collaborate with local tour operators, guides, and artisans to offer guests access to unique and authentic experiences. This could include guided tours of historical sites, workshops on local crafts, or private wine tastings.
- Shared Marketing: Cross-promotion between the inn and partner businesses can increase visibility and reach a wider audience. Inns can feature partner businesses in their marketing materials, while partner businesses can offer special promotions to inn guests.
Boosting Tourism and Revenue
Alliances can contribute significantly to promoting tourism and generating revenue for participating businesses.
- Increased Visibility: Partnerships allow businesses to leverage each other’s marketing efforts, expanding their reach and attracting a broader audience. This can lead to increased bookings for the inn and higher customer traffic for partner businesses.
- Unique Experiences: By offering unique and tailored experiences, alliances can attract discerning travelers seeking authentic local experiences. This can differentiate the destination from competitors and create a stronger brand identity.
- Economic Growth: Successful alliances can contribute to the overall economic growth of the local area. Increased tourism translates to higher revenue for businesses, creating jobs and supporting local communities.
Successful Alliances: Real-World Examples
Numerous successful alliances between bed and breakfast inns and local businesses demonstrate the benefits of this approach.
- Wine Country Inns and Vineyards: In wine regions, inns often partner with local vineyards to offer guests wine tasting experiences, vineyard tours, and special packages that include wine-themed dinners. This collaboration enhances the guest experience and attracts wine enthusiasts, driving revenue for both the inn and the vineyard.
- Coastal Inns and Water Activities: In coastal areas, inns can partner with local boat rental companies, kayaking outfitters, and scuba diving operators to offer guests access to water-based activities. This can create a unique and memorable experience for travelers seeking adventure and relaxation.
- City Inns and Cultural Attractions: In urban settings, inns can collaborate with museums, theaters, and art galleries to offer guests discounts on tickets or exclusive access to events. This can enhance the cultural experience for travelers and attract a broader audience to the inn.
Cooking and Culinary
The culinary world thrives on collaboration, and alliances play a crucial role in driving innovation, enhancing food quality, and ultimately, elevating the dining experience. From partnerships between chefs and food suppliers to collaborations between restaurants and culinary institutions, these alliances foster a dynamic exchange of knowledge, resources, and expertise, shaping the landscape of contemporary gastronomy.
Types of Alliances in the Culinary Industry
These alliances take various forms, each contributing to the growth and evolution of the culinary world:
- Chef-Supplier Partnerships: Chefs often collaborate with food suppliers to source high-quality, seasonal ingredients, ensuring freshness and flavor. These partnerships can involve exclusive contracts, joint marketing initiatives, and even collaborative menu development. For example, a renowned chef might partner with a local farm to create a signature dish featuring their unique produce, showcasing the farm’s commitment to sustainable agriculture while elevating the chef’s culinary artistry.
- Restaurant-Restaurant Collaborations: Restaurants can form alliances to share resources, expertise, and even customers. This could involve cross-promotional campaigns, guest chef dinners, or joint ventures to open new locations. For instance, two restaurants specializing in different cuisines might collaborate on a pop-up event, offering a unique fusion dining experience that attracts a wider audience.
- Restaurant-Culinary Institution Partnerships: Restaurants often partner with culinary schools or universities to provide students with real-world experience, offer internships, and even develop joint research projects. These collaborations can lead to the development of innovative dishes, improved training programs, and a more robust culinary ecosystem. For example, a Michelin-starred restaurant might partner with a culinary school to create a mentorship program, allowing students to learn from experienced chefs and gain valuable insights into the industry.
Benefits of Culinary Alliances
Alliances in the culinary world bring numerous benefits, driving innovation, enhancing food quality, and improving customer satisfaction:
- Enhanced Food Quality: Partnerships between chefs and food suppliers guarantee access to fresh, high-quality ingredients, ensuring that dishes are made with the best possible ingredients.
- Culinary Innovation: By sharing ideas and resources, chefs, suppliers, and restaurants can push the boundaries of culinary creativity, leading to the development of new dishes, techniques, and flavor combinations.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: The enhanced quality of food, innovative menu offerings, and collaborative marketing initiatives contribute to a more satisfying dining experience for customers.
- Sustainable Practices: Alliances can promote sustainable food practices, such as sourcing local ingredients, reducing food waste, and supporting ethical farming methods.
Examples of Successful Culinary Alliances
Several successful examples of alliances in the culinary industry demonstrate the power of collaboration:
- The French Laundry and Napa Valley Farms: The French Laundry, a renowned restaurant in California, has long-standing partnerships with local farms, ensuring access to the freshest and highest quality ingredients. This collaboration has resulted in a menu that showcases the best of Napa Valley’s produce and a commitment to sustainable agriculture.
- Alinea and the Institute of Culinary Education (ICE): Alinea, a three-Michelin-starred restaurant in Chicago, has partnered with ICE to provide students with real-world experience and mentorship opportunities. This collaboration has helped to bridge the gap between culinary education and professional practice, fostering a new generation of culinary talent.
- The Culinary Institute of America (CIA) and Food & Wine Magazine: The CIA, a world-renowned culinary school, has a long-standing partnership with Food & Wine Magazine, collaborating on educational programs, culinary events, and publications. This alliance has helped to elevate the profile of the CIA and promote culinary excellence through various platforms.
As technology continues to advance and healthcare delivery models evolve, healthcare alliances are poised to play an even more critical role in shaping the future of telemedicine. By fostering collaboration, sharing resources, and leveraging innovation, these alliances can help healthcare providers overcome challenges, enhance patient care, and drive the transformation of the healthcare industry.
General Inquiries
What are the main benefits of healthcare alliances in telemedicine?
Healthcare alliances offer numerous benefits in telemedicine, including shared resources, expertise, and technology infrastructure. They can help healthcare providers overcome challenges in adopting and scaling telemedicine services, leading to improved patient access, cost reduction, and enhanced care quality.
How can healthcare alliances address data security concerns in telemedicine?
Data security is paramount in telemedicine alliances. By establishing robust security protocols, implementing encryption technologies, and adhering to relevant regulations, alliances can mitigate data breaches and protect patient privacy.
What are some examples of successful healthcare alliances in telemedicine?
Numerous successful healthcare alliances have leveraged telemedicine to improve patient care and outcomes. Examples include partnerships between hospitals and telehealth companies, collaborations between healthcare providers and insurance companies, and mergers between healthcare organizations specializing in telemedicine services.





